Effective facility management is critical for ensuring safe, efficient, and sustainable operations in organizations. ISO 41001:2018, the international standard for Facility Management Systems (FMS), provides a structured framework to optimize facility-related processes, enhance productivity, and improve the overall quality of services.
This article explores the essentials of ISO 41001:2018, its benefits, practical implementation steps, and tips for achieving excellence in facility management. Whether you manage corporate offices, hospitals, educational institutions, or industrial facilities, ISO 41001:2018 offers the tools to streamline operations and create value for your organization.
What Is ISO 41001:2018?
ISO 41001:2018 is an international standard that outlines the requirements for a Facility Management System (FMS). It provides organizations with a framework to manage facilities effectively, ensuring they align with strategic goals and operational needs.
Facility management encompasses a broad range of activities, including:
- Space management
- Asset maintenance
- Energy efficiency
- Safety and compliance
- Service quality
ISO 41001:2018 helps organizations deliver consistent, efficient, and cost-effective facility management services that meet stakeholder expectations.

Why Is ISO 41001:2018 Important?
Facilities play a vital role in supporting organizational goals, productivity, and sustainability. Poor facility management can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased costs, and diminished stakeholder satisfaction. ISO 41001:2018 addresses these challenges by promoting best practices and ensuring alignment between facilities and organizational objectives.
Key Benefits of ISO 41001:2018
- Improved Efficiency Streamlining facility-related processes reduces waste, optimizes resource use, and enhances operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Satisfaction A well-managed facility creates a safe, comfortable, and functional environment for employees, customers, and other stakeholders.
- Cost Savings Proactive maintenance, energy efficiency measures, and optimized space utilization reduce operational expenses.
- Regulatory Compliance ISO 41001:2018 ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements related to safety, health, and environmental standards.
- Increased Resilience The standard promotes risk management and business continuity planning to handle disruptions effectively.
- Global Recognition Certification demonstrates a commitment to excellence in facility management, boosting credibility and competitive advantage.
Core Components of ISO 41001:2018
ISO 41001:2018 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, ensuring continual improvement in facility management processes. Key elements include:
- Context of the Organization
Understanding the internal and external factors that affect facility management, including stakeholder needs and regulatory requirements.
- Leadership Commitment
Top management must actively support and promote the FMS, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- Planning
Establishing objectives, identifying risks, and developing action plans to achieve desired outcomes.
- Support
Providing resources, training, and tools to implement and maintain the FMS effectively.
- Operational Control
Managing day-to-day facility operations, including maintenance, safety, and service delivery.
- Performance Evaluation
Monitoring, measuring, and analyzing facility management performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Continual Improvement
Implementing changes to enhance the FMS and address emerging challenges.
Steps to Implement ISO 41001:2018
- Understand the Standard
Familiarize yourself with ISO 41001:2018 requirements and how they align with your organization’s objectives. Consider training sessions or consulting experts for guidance.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
Evaluate your current facility management practices to identify gaps between existing processes and the standard’s requirements.
- Define Scope and Objectives
Determine the scope of your FMS and set clear objectives that align with organizational goals and stakeholder expectations.
- Develop a Facility Management Policy
Create a formal policy outlining your commitment to effective facility management, with measurable goals and objectives.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define roles and responsibilities within the FMS to ensure accountability and effective implementation.
- Implement Operational Controls
Establish processes for critical activities such as maintenance, safety checks, energy management, and vendor management.
- Train Employees
Provide training to employees to ensure they understand their roles in maintaining and improving the FMS.
- Monitor and Measure
Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of facility management processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Conduct Internal Audits
Regular audits help identify non-conformities and provide opportunities for enhancement.
- Certification Audit
Engage an accredited certification body to assess your FMS and issue ISO 41001:2018 certification upon compliance.
Examples of ISO 41001:2018 in Action
Case Study: Corporate Office
A multinational corporation implemented ISO 41001:2018 to improve space utilization and energy efficiency across its offices. By integrating smart building technologies and optimizing maintenance schedules, the company reduced energy costs by 30% and increased employee satisfaction.
Case Study: Healthcare Facility
A hospital adopted ISO 41001:2018 to enhance patient safety and service quality. Proactive maintenance of medical equipment and compliance with health and safety regulations led to a 25% reduction in operational disruptions.
Practical Tips for ISO 41001:2018 Implementation
- Leverage Technology Use facility management software to automate processes, monitor performance, and generate actionable insights.
- Engage Stakeholders Involve employees, contractors, and other stakeholders in the FMS to ensure alignment and effective collaboration.
- Focus on Sustainability Implement energy-efficient solutions, waste reduction initiatives, and sustainable practices to enhance environmental performance.
- Conduct Regular Reviews Periodically review facility management policies and processes to adapt to changing needs and emerging challenges.
- Start with High-Impact Areas Prioritize critical areas such as safety, energy management, or maintenance to demonstrate quick wins and build momentum.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Resistance to Change
Employees or contractors may resist new processes. Address this by involving them early and providing adequate training.
- Resource Constraints
Smaller organizations may face budgetary or staffing limitations. Focus on scalable solutions and prioritize high-impact areas.
- Maintaining Compliance
Regularly update your FMS to stay compliant with evolving regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
ISO 41001:2018 provides a comprehensive framework for organizations seeking to optimize facility management and deliver value to stakeholders. By implementing this standard, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service quality while ensuring sustainability and resilience.
Whether you manage a corporate office, hospital, or industrial facility, adopting ISO 41001:2018 can transform your facility management practices and position your organization as a leader in the industry. Start your journey today and unlock the benefits of effective facility management.
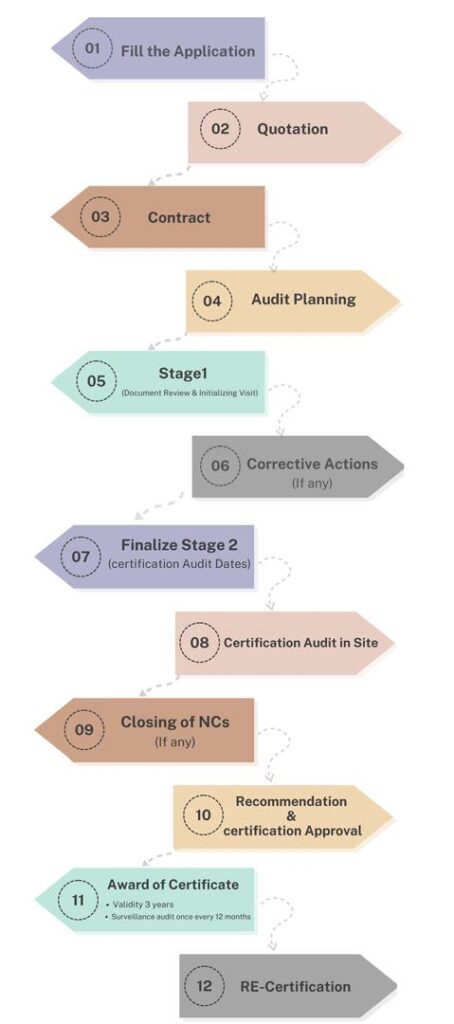
Certification Process
1- Completion of information related to the company name, company activities, the number of staff per work shift, website address, and branches.
2- Announcement of costs related to the requested certification issuance process.
3- Preparation and approval of the contract for implementation.
4- Planning the audit process and notifying the client for audit process.
5- reviewing documents to identify the client strengths and weaknesses in comparison to the established documentation.
6- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses.
7- Final planning for conducting the audit, registration, and certification issuance.
8- Conducting the on-site audit process at the client by the specialized team of the certifying company.
9- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses in the execution of the organization’s processes.
10- Recommendation for the issuance of a certification related to the client to the head office.
11- Achieving the related certification.
12- Renew after three years.