In today’s world, businesses are expected to go beyond profit-making and contribute to societal well-being and environmental sustainability. ISO 26000:2010, the international standard for social responsibility, provides a framework to help organizations operate in a socially responsible manner. Unlike other ISO standards, ISO 26000 is not certifiable but serves as a guideline for organizations committed to ethical and sustainable practices.
This article explores the fundamentals of ISO 26000:2010, its core principles, benefits, implementation strategies, and practical tips to help organizations enhance their social responsibility efforts.
What Is ISO 26000:2010?
ISO 26000:2010 is an international standard that provides guidance on integrating social responsibility into organizational practices. It helps businesses understand and address societal and environmental impacts, promoting ethical, transparent, and sustainable operations.
Key Features of ISO 26000:2010
- Voluntary: ISO 26000 is not a certifiable standard but serves as a guideline for organizations.
- Broad Applicability: The standard applies to all types of organizations, regardless of size, location, or sector.
- Holistic Approach: It covers various aspects of social responsibility, including governance, labor practices, environmental impact, and community involvement.

Why Is ISO 26000:2010 Important?
Organizations are increasingly held accountable for their impact on society and the environment. ISO 26000:2010 provides a structured approach to meeting these expectations, ensuring sustainable success and stakeholder trust.
Key Benefits of ISO 26000:2010
- Enhanced Reputation Adopting socially responsible practices builds trust and enhances an organization’s reputation among customers, employees, and stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Engagement The standard encourages organizations to engage with stakeholders, fostering better relationships and mutual understanding.
- Compliance with Regulations ISO 26000 aligns with global sustainability goals and helps organizations comply with local and international regulations.
- Sustainable Growth Social responsibility contributes to long-term growth by addressing environmental, social, and economic challenges.
- Employee Satisfaction Ethical practices and a positive workplace culture improve employee morale, retention, and productivity.
- Market Advantage Businesses committed to social responsibility often gain a competitive edge in attracting socially conscious customers and investors.
Core Principles of ISO 26000:2010
ISO 26000:2010 outlines seven core principles that guide organizations toward social responsibility:
- Accountability Organizations must take responsibility for their actions and their impact on society and the environment.
- Transparency Open communication about decisions, activities, and impacts is essential for building trust.
- Ethical Behavior Adhering to moral values and principles ensures fairness and integrity in operations.
- Respect for Stakeholder Interests Understanding and addressing the needs and expectations of stakeholders is key to building strong relationships.
- Respect for the Rule of Law Compliance with laws and regulations is a fundamental aspect of social responsibility.
- Respect for International Norms of Behavior Organizations should align with global ethical standards, even in the absence of local regulations.
- Respect for Human Rights Protecting and promoting human rights is a cornerstone of social responsibility.
Key Areas of ISO 26000:2010
ISO 26000:2010 focuses on seven core areas of social responsibility:
- Organizational Governance
Good governance practices, including ethical decision-making and accountability, are crucial for social responsibility.
- Human Rights
Organizations should respect and promote human rights, ensuring non-discrimination and fair treatment.
- Labor Practices
Fair labor practices, including safe working conditions, employee development, and equitable wages, are essential.
- Environment
Organizations must minimize their environmental footprint by adopting sustainable practices and reducing waste.
- Fair Operating Practices
Integrity in business dealings, including anti-corruption measures and fair competition, fosters trust and fairness.
- Consumer Issues
Ensuring product safety, transparency, and customer satisfaction builds strong consumer relationships.
- Community Involvement and Development
Engaging with and contributing to local communities enhances societal well-being and strengthens organizational impact.
Steps to Implement ISO 26000:2010
- Understand the Standard
Gain a thorough understanding of ISO 26000:2010’s principles and core subjects. Training sessions or workshops can help key personnel grasp its concepts.
- Assess Current Practices
Conduct a self-assessment to identify gaps between current practices and ISO 26000 guidelines.
- Engage Stakeholders
Identify and involve key stakeholders to understand their expectations and gather feedback on your social responsibility initiatives.
- Develop a Strategy
Create a social responsibility strategy that aligns with organizational goals and addresses key areas for improvement.
- Set Objectives
Define measurable objectives and targets to track the progress of your social responsibility efforts.
- Implement Changes
Incorporate ISO 26000 principles into daily operations, including policies, processes, and decision-making.
- Monitor and Report
Track progress using key performance indicators (KPIs) and communicate results transparently to stakeholders.
Examples of ISO 26000:2010 in Action
Case Study: Retail Sector
A global retailer adopted ISO 26000:2010 to enhance its sustainability practices. By sourcing materials ethically and reducing plastic packaging, the company improved customer trust and reduced its environmental impact.
Case Study: Manufacturing Industry
A manufacturing firm used ISO 26000:2010 guidelines to improve worker safety and community engagement. The initiative led to a 30% reduction in workplace incidents and strengthened relationships with local stakeholders.
Practical Tips for ISO 26000:2010 Implementation
- Leverage Technology Use digital tools to monitor and report on social responsibility initiatives, such as environmental impact and stakeholder engagement.
- Start Small Focus on high-priority areas that align with your organizational values and scale efforts over time.
- Foster a Culture of Responsibility Engage employees at all levels to embed social responsibility into your organization’s culture.
- Collaborate with Partners Work with suppliers, customers, and community organizations to amplify the impact of your initiatives.
- Communicate Progress Regularly update stakeholders on your achievements and future goals to maintain transparency and trust.
Conclusion
ISO 26000:2010 offers a valuable framework for organizations striving to operate responsibly and sustainably. By adopting its principles, businesses can create a positive impact on society and the environment while enhancing their reputation and long-term success.
Whether you’re a small business or a multinational corporation, embracing social responsibility through ISO 26000:2010 is a step toward a brighter, more sustainable future. Start today to make a difference and inspire trust among your stakeholders.
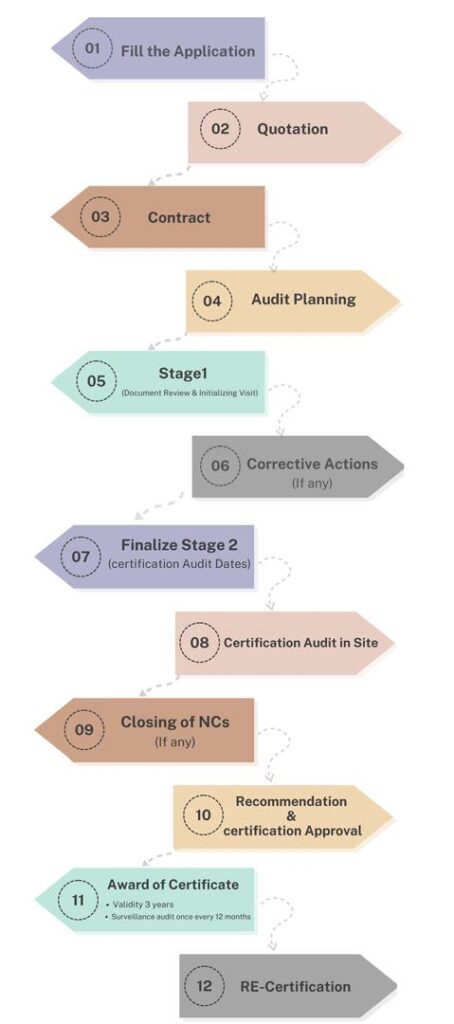
Certification Process
1- Completion of information related to the company name, company activities, the number of staff per work shift, website address, and branches.
2- Announcement of costs related to the requested certification issuance process.
3- Preparation and approval of the contract for implementation.
4- Planning the audit process and notifying the client for audit process.
5- reviewing documents to identify the client strengths and weaknesses in comparison to the established documentation.
6- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses.
7- Final planning for conducting the audit, registration, and certification issuance.
8- Conducting the on-site audit process at the client by the specialized team of the certifying company.
9- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses in the execution of the organization’s processes.
10- Recommendation for the issuance of a certification related to the client to the head office.
11- Achieving the related certification.
12- Renew after three years.