Food safety is a top priority for organizations involved in the food supply chain. Ensuring the safety of food products not only protects public health but also strengthens consumer trust and business reputation. ISO 22000:2018, the international standard for food safety management systems (FSMS), provides a robust framework for managing food safety risks and ensuring compliance with global standards.
This article delves into the essentials of ISO 22000:2018, its benefits, practical implementation steps, and tips for achieving certification. Whether you’re a food producer, processor, or distributor, understanding this standard is key to ensuring food safety and building trust in your brand.
What Is ISO 22000:2018?
ISO 22000:2018 is an internationally recognized standard for food safety management systems. It specifies requirements for organizations to identify, manage, and control food safety hazards across the food supply chain. The standard integrates key elements such as:
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- Risk management and continual improvement.
ISO 22000:2018 is applicable to organizations of all sizes, including farmers, processors, retailers, and food service providers.

Why Is ISO 22000:2018 Important?
Food safety breaches can lead to severe consequences, including health risks, product recalls, and reputational damage. ISO 22000:2018 addresses these challenges by providing a systematic approach to identifying and mitigating food safety hazards.
Key Benefits of ISO 22000:2018
- Enhanced Food Safety A robust FSMS ensures that food products are safe for consumption, minimizing risks of contamination and foodborne illnesses.
- Regulatory Compliance ISO 22000:2018 helps organizations comply with local and international food safety regulations, reducing legal risks.
- Improved Customer Confidence Certification demonstrates your commitment to food safety, boosting consumer trust and loyalty.
- Streamlined Processes The standard promotes efficient processes, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- Global Recognition ISO 22000:2018 certification is recognized worldwide, facilitating trade and market access.
Key Elements of ISO 22000:2018
ISO 22000:2018 is built on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle and integrates the principles of HACCP. Key components include:
- Context of the Organization
Understanding internal and external factors that affect food safety, such as regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
- Leadership Commitment
Top management must take responsibility for the FSMS, demonstrating leadership and accountability.
- Risk-Based Thinking
A proactive approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating food safety hazards.
- Communication
Effective communication across the supply chain to ensure transparency and collaboration.
- Operational Controls
Implementing controls at critical points in the food production and handling processes.
- Performance Evaluation
Regular monitoring, measurement, and auditing to ensure the effectiveness of the FSMS.
- Continual Improvement
Ongoing efforts to enhance the FSMS based on performance data and feedback.
Steps to Implement ISO 22000:2018
- Understand the Standard
Familiarize yourself with ISO 22000:2018 requirements and how they align with your organization’s goals. Training or consulting services can provide valuable insights.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
Assess your current food safety practices to identify gaps between existing processes and ISO 22000:2018 requirements.
- Develop a Food Safety Policy
Create a formal policy outlining your commitment to food safety and compliance with the standard.
- Conduct Hazard Analysis
Identify potential food safety hazards and establish preventive controls using HACCP principles.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities
Assign clear roles and responsibilities for food safety management within your organization.
- Train Employees
Provide training to employees on food safety practices, hygiene, and their roles in maintaining the FSMS.
- Implement the FSMS
Put the FSMS into action, ensuring all processes and controls are properly documented and followed.
- Monitor and Measure
Regularly monitor critical control points, evaluate performance, and take corrective actions as needed.
- Conduct Internal Audits
Internal audits help identify non-conformities and provide opportunities for improvement.
- Certification Audit
Engage a certification body to assess your FSMS and issue ISO 22000:2018 certification upon compliance.
Examples of ISO 22000:2018 in Action
Case Study: Food Processing Company
A mid-sized food processing company implemented ISO 22000:2018 to address food safety risks. By improving hygiene practices and automating critical control point monitoring, they reduced contamination incidents by 30% and gained certification, boosting client confidence.
Case Study: Restaurant Chain
A global restaurant chain adopted ISO 22000:2018 to standardize food safety practices across locations. The implementation led to consistent quality and safety standards, enhancing customer trust and loyalty.
Practical Tips for ISO 22000:2018 Implementation
- Leverage Technology Use digital tools for monitoring critical control points, managing documentation, and automating reporting.
- Engage Suppliers Collaborate with suppliers to ensure they meet your food safety standards, as they play a crucial role in the supply chain.
- Focus on Training Continuous employee training is essential to maintain food safety standards and prevent lapses.
- Document Everything Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance and facilitate audits.
- Start Small Begin with a pilot project or focus on high-risk areas before scaling the FSMS across your organization.
Challenges and Solutions
- Resistance to Change
Employees may resist new processes. Address this by involving them early in the implementation process and emphasizing the benefits.
- High Initial Investment
Implementation costs can be a barrier. Prioritize high-impact areas and explore funding options to offset costs.
- Maintaining Compliance
Regular audits and reviews are essential to stay compliant. Use performance metrics and feedback to guide improvements.
Conclusion
ISO 22000:2018 is a critical standard for organizations committed to food safety and quality. By implementing this framework, businesses can enhance safety practices, meet regulatory requirements, and build trust with consumers.
Whether you’re new to ISO standards or seeking to upgrade your FSMS, ISO 22000:2018 offers the tools to safeguard your brand and deliver safe, high-quality food products. Start your journey today and position your organization as a leader in food safety.
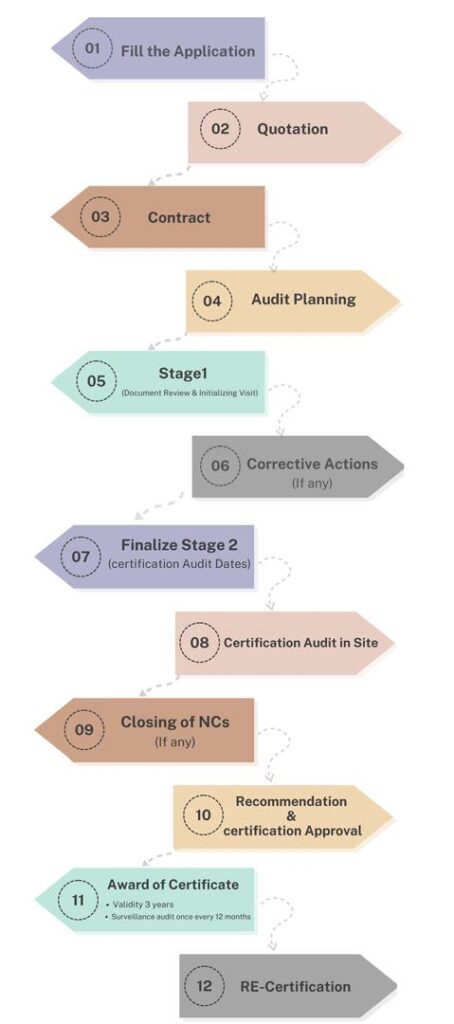
Certification Process
1- Completion of information related to the company name, company activities, the number of staff per work shift, website address, and branches.
2- Announcement of costs related to the requested certification issuance process.
3- Preparation and approval of the contract for implementation.
4- Planning the audit process and notifying the client for audit process.
5- reviewing documents to identify the client strengths and weaknesses in comparison to the established documentation.
6- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses.
7- Final planning for conducting the audit, registration, and certification issuance.
8- Conducting the on-site audit process at the client by the specialized team of the certifying company.
9- Corrective actions for potential weaknesses in the execution of the organization’s processes.
10- Recommendation for the issuance of a certification related to the client to the head office.
11- Achieving the related certification.
12- Renew after three years.